These days, all cars have a component that they rarely had prior to 1975—catalytic converters. While most people are aware that their vehicle has one, many of them have no idea what they are, how they work, or what purpose they serve. It’s important to understand this part of your car, so we’ll go over everything you need to know about the emission-regulating component in this article.
- Catalytic Converters – The Basics
- What Does A Catalytic Converter Look Like?
- Why Does A Car Require A Catalytic Converter?
- How Does A Catalytic Converter Work?
- How Long Will A Catalytic Converter Last?
- What Can Cause Problems With A Catalytic Converter?
- What Are The Signs That A Catalytic Converter Is Defective?
- Should I Clean My Catalytic Converter Myself?
- How Much Does It Cost To Replace A Catalytic Converter?
- Can I Remove My Car’s Catalytic Converter?
Catalytic Converters – The Basics
Catalytic converters are devices that use a catalyst in order to convert harmful compounds found in car exhaust into less harmful alternatives. The three compounds that are converted by the catalytic converter are:
- Nitrogen oxides: these are created when the engine’s heat forces nitrogen in the air to mix with oxygen.
- Carbon monoxide: this is created by gasoline is combusted.
- Hydrocarbons: this comes in the form of gasoline that remains unburned.
These three compounds are harmful for different reasons. Hydrocarbons are known to produce smog, as is nitrogen oxide, which also causes acid rain. Meanwhile, carbon monoxide is poisonous for any creature that breathes air containing it.
The catalytic converter has a catalyst (which usually takes the form of platinum, palladium, and rhodium) that is coated onto ceramic beads or a ceramic honeycomb housed inside a muffler-like package fixed onto the car’s exhaust pipe. This catalyst then aids the process of converting the carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons into water and carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxide into oxygen and nitrogen.
By controlling harmful emissions, catalytic converters are a key component in your vehicle. However, it’s still important to understand how they work and what you’ll need to do if they break down. We’ll also go over how to detect potential issues with your catalytic converter and discuss how to ensure your converter operates properly for as long as possible.
What Does A Catalytic Converter Look Like?
A Catalytic converter has a similar appearance to an exhaust silencer, but it is slimmer and smaller. On a modern vehicle, the catalytic converter will usually be located close to the car’s engine to allow it to warm up more rapidly. This is because catalytic converters are more efficient if they are hot, and so it makes more sense to locate them in this high-temperature area of the car.
Why Does A Car Require A Catalytic Converter?
Car exhausts produce toxic emissions that cause damage to our environment when they’re released, leading to problems like acid rain and smog. For more than half a century, car manufacturers have been working on finding new ways of reducing the pollutants and gases that vehicles cause. Cars that were made before 1975 do not have a catalytic converter, but that year saw the popularization of this invention. A few laters later, in 1981, all new vehicles sold in the United States began to be legally required to contain the component. Since then, it’s been nearly impossible to find a car without one. Today, catalytic converters are one of the most vital components inside your vehicle’s emission control system.
How Does A Catalytic Converter Work?
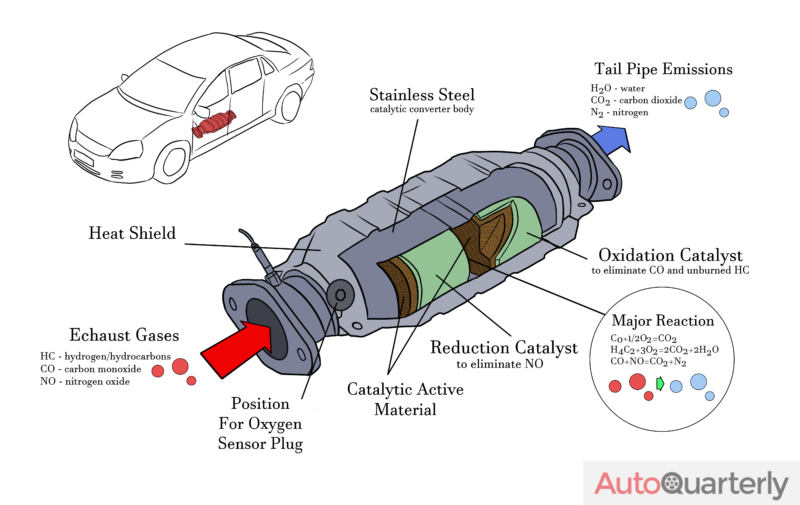
Your car’s catalytic converter has a metal casing holding two ceramic blocks composed of thousands of micro-cellular channels, taking a similar shape to a honeycomb. The ceramic blocks have surfaces that have precious metal coatings of palladium, rhodium, and platinum. When the blocks and their coating heat up, a chemical reaction takes place that breaks the toxic gases down, converting them into water vapor and carbon dioxide and then releasing these harmless compounds into the air.
How Long Will A Catalytic Converter Last?
You can usually expect your catalytic converter to last for a minimum of ten years, or around 70,000 to 100,000 miles. There are exceptions, though. If you only use your car for brief start-and-stop journeys, it’s possible that your catalytic converter may wear out more rapidly since the catalytic converter and the engine won’t reach their ideal operating temperatures before the journey comes to an end and the engine is switched off.
Although a catalytic converter generally will have quite a long lifespan, it will still need to be occasionally checked for external or internal damage. Regular inspection and maintenance are important, since a faulty catalytic converter will not only harm the environment, but be costly to repair.
What Can Cause Problems With A Catalytic Converter?
Although catalytic converters should last a long time, there are a number of problems that can occur that will cause them to malfunction or break down. These include:
- Physical damage.
- Contamination
- Overheating.
- Carbon deposits building up inside causing clogging.
Contaminants like coolant and oil may end up leaking into the car’s engine. The fluids can then clog the catalytic converter and restrict the gases that pass through the car’s exhaust. When the exhaust flow becomes hampered, a lower volume of air is able to get into the car’s engine, which prevents the vehicle from performing at its most efficient level.
Catalytic converters may also overheat. This can be due to an excessive amount of unburned fuel entering into the catalytic converter because of leaky exhaust valves or misfiring spark plugs.
Another component that may malfunction is the lambda sensor, a component in the car that monitors the level of oxygen inside the exhaust system. The exterior of your catalytic converter may also experience physical damage caused by speed bumps, bumping a curb, hitting road debris, or getting into an accident..
What Are The Signs That A Catalytic Converter Is Defective?
There are a number of symptoms to look out for that will indicate that your car’s catalytic converter is defective or broken. These signs include:
- Sluggish or poor engine performance.
- A reduction in acceleration and power.
- Dark-colored exhaust smoke.
- A sulfurous smell like rotten eggs being emitted from the car exhaust.
- A lot of heat underneath the car.
Luckily, the majority of modern vehicles are equipped with diagnostics onboard that use an oxygen sensor in order to detect any changes in the fumes that are emitted from the car’s exhaust. If the catalytic converter isn’t functioning properly, a dashboard light or other indicator will indicate the problem. If you see this dashboard light or notice any of the other symptoms that indicate a potential problem, you should immediately arrange for your vehicle to be taken to a service center or garage to be inspected and, if necessary, repaired.
Should I Clean My Catalytic Converter Myself?
If your car’s catalytic converter is not functioning properly, an excessively high amount of harmful gases and emissions will come out of its exhaust. This is very damaging to the environment, and even contributes to the global problem of climate change. With this in mind, some drivers wonder whether they should clean their vehicle’s catalytic converter themselves. This is especially pertinent for any driver who primarily only undertakes short journeys, as their converters are more likely to malfunction.
You can purchase a fuel system cleaner that you can use yourself in automotive supplies stores, or, alternatively, you can take the vehicle to a garage or service center offering exhaust cleaning services. This will help to ensure that your vehicle’s emissions levels don’t exceed acceptable standards. You can also prevent any issues with your exhaust system from occurring at all by taking longer trips where you’re able to drive at speed. When you follow these recommendations, you will be taking all reasonable steps to ensure your vehicle’s catalytic converter stays in good working order for as long as possible.
How Much Does It Cost To Replace A Catalytic Converter?
It can be extremely costly to replace your car’s catalytic converter. This is because expensive precious metals like palladium and platinum are used in their construction. The price will significantly vary depending on which type of car you have, its individual engine and the type of catalytic converter that it has been fitted with. However, you can expect the cost to run into hundreds or even thousands of dollars should you require a new one to be fitted on your vehicle, particularly if the catalytic converter is designed to be an integral component of your car’s exhaust manifold. Therefore, it couldn’t be more vital to arrange for your catalytic converter to be checked on a regular basis to ensure that it doesn’t develop a fault or a problem that could eventually necessitate its replacement.
Can I Remove My Car’s Catalytic Converter?
Some drivers wonder whether they should remove their vehicle’s catalytic converter, since this could increase its horsepower and the amount of mileage you can get from your fuel. Your exhaust may also sound better if the converter is removed. It’s important to be aware, though, that in America and most other countries you are forbidden by law from removing your car’s catalytic converter unless you have a valid reason to do so. There is a considerable amount of legal procedure to go through if you wish to prove that you have a reason for the removal, so this isn’t something that we recommend. If your car is on the road without a catalytic converter, you may be fined severely and your vehicle may even be seized. On top of this, you will also be emitting an unnecessary level of toxic and dangerous gases into the environment, contributing to a worsening of our already severe environmental problems.


