The functionality of your car’s airbag is probably the last thing on your mind when you’re driving, but knowing how much of a difference they make in accidents could make you think twice. It’s not pleasant to know that you may be facing the steering wheel head-on in case of an accident, but before the 1950s, riding without one of these life-saving devices was the norm.
Thankfully, because of today’s advancements in vehicle safety technology, most people go through their whole lives without experiencing an accident that is bad enough to trigger their car’s airbag system. Unless you’ve been in such a situation before, you may not know the exact price of airbags. Unfortunately, this isn’t as simple as an oil change. Depending on the model of your car, it can be a costly procedure.
In this guide, we´ll walk you through everything you need to consider before replacing an airbag and exactly what goes into the cost.
How Much Does Airbag Replacement Cost?
It’s hard to estimate the exact cost of replacing an airbag system because it is dictated by the car’s brand, model, and the type of airbags used. In most cases, replacement work can easily cost up to a couple of thousand dollars.
Example Airbag Replacement Costs
To give you some perspective, let’s break down the average cost of airbag replacement on a Ford F-Series, currently one of the best-selling cars in the United States. Completely replacing one of the airbag modules on a Ford F-Series will cost roughly $600.
The airbag system alone will cost about $400. Still, you need to account for the mechanic and other replacement parts that may have been damaged by the deployment of the safety device itself, including any damage sustained to the front paneling, the dashboard, or the steering wheel.
You will also need to account for every airbag module that has been deployed in the car, which could be up to five, making the whole ordeal cost around $3,000 for this particular model.
Factors That Influence the Cost of Airbag Replacements
Here are other things you should consider when replacing the airbag that may have an impact on the cost.
- Usually, you’re not just replacing the airbag module but many of the individual components that make up the whole safety system, like the speed sensors, springs, and paneling. For instance, if your car’s airbag is built into the steering wheel, you may have to replace the whole wheel altogether.
- It is possible to source the components cheaply online. However, this doesn’t mean your mechanic will install them. They may have their own supplier. Also, the mechanic may not be familiar with the type of airbag you bought. People don’t just go to the surgeon with their own hip replacements.
- Airbags bought online are unlikely to come with the same kind of warranty your mechanic or car manufacturer may offer you, which plays a vital role in insurance policy and coverage.
Airbags and the Insurance Myth
There are many widespread myths regarding airbags, from their efficiency to how they impact the legal status of your car. For instance, it’s sometimes said that insurance companies will just classify the car as totaled if an airbag goes off. This is not true.
While older models are indeed more likely to get written off as totaled, it’s because the cost of repairing the whole airbag system sometimes exceeds that of the vehicle, so performing repairs is not a cost-effective solution. Declaring a car as totaled is more of a mathematical question rather than a mechanical one. Most states consider a car totaled if the damage exceeds 70 or 80 percent of the vehicle’s total cash value.
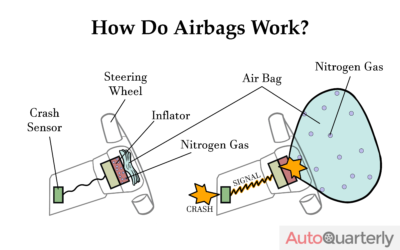
How Do Airbags Work?
You may think that knowing how the airbag system sensors capture precise movements or the complexity of the chemical reaction that deploys the cushion is entirely irrelevant to your need to repair the actual thing. But certain aspects of its functionality and the parts involved do tend to impact the replacement cost. Plus, it’s kind of cool to know how these almost magical life-saving devices behind our steering wheels can deploy in a mere 0.55 seconds after a severe impact.
Airbags were first designed to replace seat belts, but people quickly realized that it was better to combine both devices. In fact, in 1973 the Ford car company, General Motors, launched the first-ever experimental airbag fleet. It was initially only meant for government use, but it paved the way for modern safety devices.
Essentially, an airbag deploys when its sensor captures sudden deceleration or impact at certain speeds. The specific velocity that causes the device to trigger changes from country to country. In the United States, the NHTSA considers this to be the equivalent of hitting a solid object at approximately 8 to 14 mph. However, specific numbers may vary among car manufacturers.
When these sensors register the sudden change in speed or impact, the mechanism triggers an almost instant chemical reaction which, in a matter of milliseconds, expands the cushions behind the car panels to protect the person behind them. Then, nitrogen gas escapes through the holes in the bag and deflates it. For a more visual explanation of this gas reaction, check out this video from Reactions.
What Makes up an Airbag System
Airbag systems are not just a cushion and a gas pump glued together, but a complex set of sensors and modules designed to work under specific conditions so that it doesn’t go off from hitting a bump on the road or breaking suddenly. Sometimes it’s just specific parts that need to be repaired, but depending on the module, it may be necessary to change the whole system.
What does that involve exactly? Well, if we take an airbag system apart, we’re likely to find similar components across models, including the following.
- The Igniter: This is the mechanism that starts the chemical reaction that is responsible for inflating the cushions.
- Warning Light: This is usually located on the dashboard, and is designed to let you know if there’s anything wrong with the airbag or if it has been deployed.
- Clockspring: This piece allows the steering wheel to rotate and the horn to function, while still being connected to the airbag system.
- Pyrotechnic Inflator: This is where the gas for the chemical reaction is contained.
- Seatbelt Pretensioner: A piece designed to retract the seat belt to keep passengers in place in case of a collision.
- ECU: The electronic control unit houses the sensors and electrical parts that evaluate velocity and deceleration. In short, this part of the system decides if the airbag needs to be deployed.
Generally speaking, when an airbag is deployed, most of its components need to be replaced.

Airbag Types and Durability
Airbags come in all kinds of shapes and sizes that are continually being replaced with more efficient models. For this reason, the replacement of different types of airbags brings with it different costs. But to make matters simple, airbags often classified by their location in the car.
The Types of Airbag
The most common types of airbags are as follows.
- Front: This is the most common type, which protects the driver and is generally located on the steering wheel.
- Side: Sometimes offered as optional, there are various types of side-impact airbags or SABs. Each one is designed to protect specific parts of the body.
- Knee: People involved in severe high-speed collisions tend to damage their knees quite often. To mitigate this, car companies started implementing knee-level systems. However, the model’s benefits are still up for debate, with some studies contradicting their actual effectiveness.
- Rear: Designed to protect the people in the back, these models prevent collision between passengers or their side of the door.
Airbag Types Are Vehicle Dependent
Remember, not every car comes equipped with all of these measures. The more security devices you have, the more protected you’re likely to be in an accident. However, you’re also more likely to spend more money replacing these systems.
Other types of airbags tend to be more uncommon or vehicle-dependent, such as the seat belt airbags and pedestrian airbags that Volvo started implementing in 2012 to mitigate damage. There are even motorcycle airbags.
How Durable Are Airbags?
Modern airbags tend to last through a car’s whole lifetime. Certain brands like Skoda encourage checkups every 14 years or so, but at that point, the cost of replacing the airbag may very well outdo that of the car.
However, this is not the case with older models. If your vehicle predates 1990, some manufacturers may advise you to replace the airbags as part of general maintenance.
Safety and Legality
Replacing an airbag system after a collision is, first and foremost, a matter of safety. A study published by the National Highway Traffic Safety Association (NHTSA) shows that front airbags reduce driver fatalities by 29% and passengers age 13 and older by 32%.
However, replacing your car’s airbags is also a matter of compliance with insurance and state law.
Legal Compliance
This is not a good time to try and wing it. Airbags in the driver and passenger seats have been mandatory in the United States since 1991. Do not drive a car without an airbag – or with a malfunctioning one. Your insurance company likely won’t cover any damage that it sustains if the vehicle is not up to technical standards, which could impact your financial wellbeing. Depending on the state, driving a car with deployed airbags may be prohibited.
DIY Replacements
With cost in mind, it may be tempting to try and DIY the airbag replacement on your own, but this is not something you can do safely without proper training. You could be seriously injured or end up further damaging the car and increasing the repair costs.
It doesn’t matter how many YouTube videos you’ve already watched – it’s always better to let a certified professional repair or replace your car’s airbag. Manipulating these devices is dangerous and, without the right knowledge, you’re likely to injure yourself or further damage the vehicle. In Germany, airbags are considered harmful explosives, so only mechanics with specific training and certifications can repair or replace them.
The more security measures you implement while driving, the better. Make sure to always use your seatbelts; we’re not living in the ‘50s when their use was not taken as seriously as today. At the end of the day, replacing your car’s airbag system goes beyond passing the required safety guideline and being in compliance with the law. It’s a matter of safety.
Final Thoughts
Changing airbag systems is a complicated and costly affair. Many variables play a hand in the price of the replacement, but in most cases, you should be ready to spend a fair amount of money.
Motor companies are continually innovating and pushing for stronger safety measures in vehicles. Although they may be costly to replace, they may save your life one day, and you can’t put a price on that.